01
/
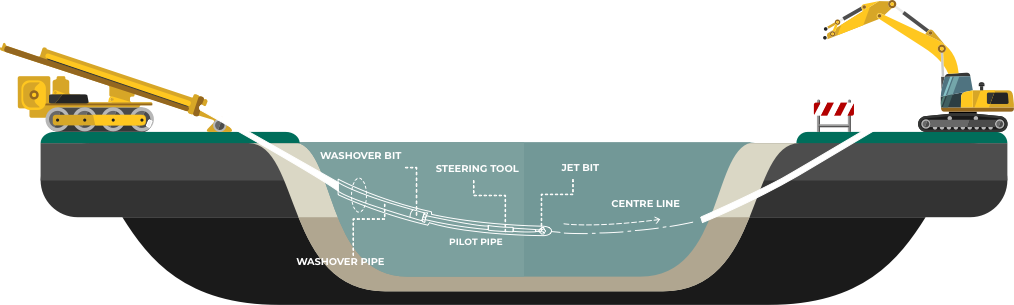
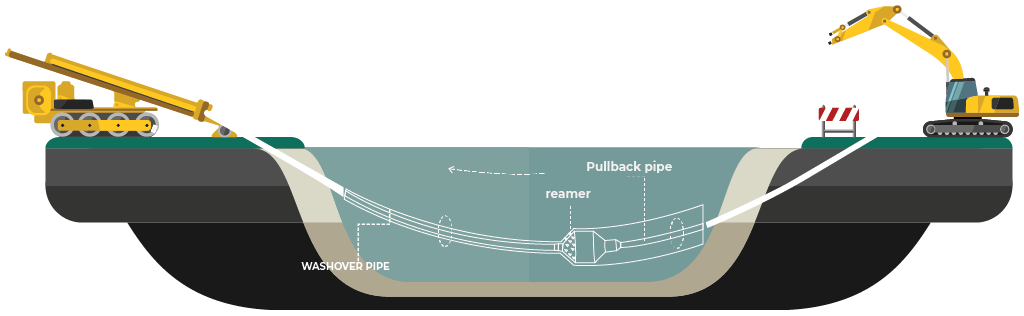
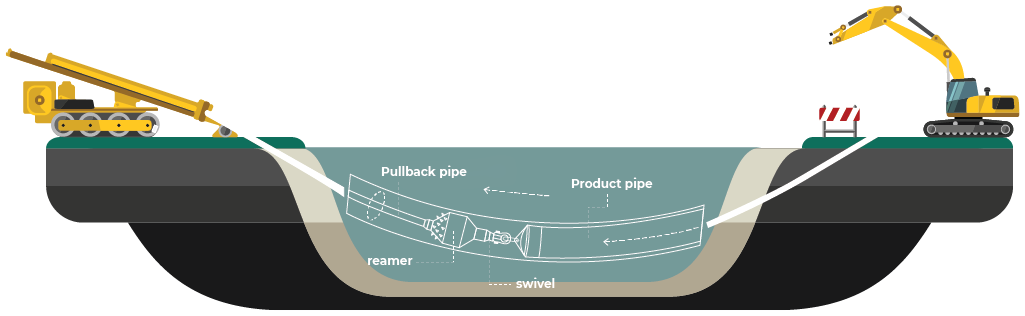
Horizontal Directional Drilling (HDD) is an advanced steerable trenchless technology, used around the globe for the installation of underground utilities along a predesigned bore path. Services include cables, gas lines, crude oil lines, sewer lines, water lines, shore approaches as well as other environmental applications. HDD is particularly useful within settings where the installation of infrastructure utilities by traditional methods, such as trenching or excavation, is not possible. The process requires minimal restoration and leaves an almost negligible impact on the surrounding environment. HDD offers a solution that is more economic, flexible and even quicker-to-finish than other open-cut methods.
HDD TECHNOLOGY.
The trenchless installation of pipes and cables using the horizontal directional drilling (HDD) method has become a recognized alternative installation in open trenches. Environmentally safe materials makes directional drilling the method of choice on environmental remediation projects and is perfect for utility installations in congested urban environments. Due to the technical advantages of the technology, the minimum adverse effect on the ground surface and its economic efficiency, the (HDD) method is widely used. The practice shows, that application of this technology reduces the operating costs of a traditional technology by a factor of 2 to 3. This method of operation is considerably faster than conventional methods, which means that the job is completed in many instances without people in the area being aware it has been done.
DO YOU HAVE A PROJECT IN MIND?
PIPE SIZE.
Any size of pipes can be utilized.
SURFACE OBSTACLES.
HDD is unaffected by surface obstacles.
ENVIROMENTAL IMPACT.
HDD has minimal impact on landscapes and no disruption to streets.
SERVICE EFFECIENCY.
HDD is cost and time efficient
WORKING AREA.
Working area is limited to the drill entry and exit points